




About Radiation Therapy
Introduction to Radiation Oncology
Radiation has been an effective tool for treating cancer for more than 100 years. Radiation oncologists are doctors trained to use radiation to eradicate cancer.About two-thirds of all cancer patients will receive radiation therapy as part of their treatment.
What Is Radiation Therapy?
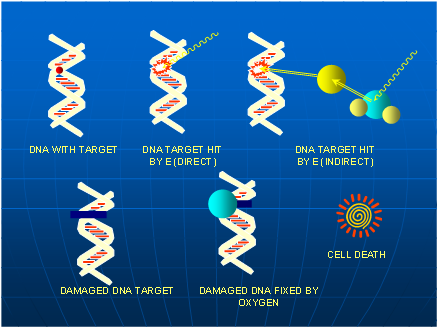
Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA within cancer cells with high energy radiation and destroying their ability to reproduce. When the damaged cancer cells are destroyed by radiation, the body naturally eliminates them. Normal cells can be affected by radiation, but they are able to repair themselves.
How Is Radiation Therapy Used?
Radiation therapy is used two different ways.
To cure cancer:
- Destroy tumors that have not spread to other body parts.
- Reduce the risk that cancer will return after surgery or chemotherapy.
- To treat the cancers which have recurred after successful previous treatments either by surgery/chemotherapy/radiation.
To reduce symptoms:
Shrinking tumors affecting quality of life, like tumors that cause shortness of breath, pain,difficulty on swallowing, intestinal obstruction.This is often referred as palliative radiation
External beam radiation therapy is used to treat manycancers , includingHead & Neck Cancers,Breast cancers,Lung Cancers,Brain tumours,Colorectal cancers,Genitourinary cancers,Skin cancers,Blood and Bone cancers.
Sometimes radiation therapy is the only treatment a patient needs.Other times, it is combined with other treatments, like surgery and chemotherapy
Radiation Oncologist
- The doctor whois specially trained to treat cancer with radiation,oversees the radiation therapy treatments.
Medical Radiation Physicist
- Ensures that complex treatment plans are properly tailored for each patient.
Dosimetrist
- Works with the radiation oncologist and medical physicist to calculate the proper dose of radiation given to the tumor.
Radiation Therapist
- Administers the daily radiation under the doctor’s prescription and supervision.
Radiation Oncology Nurse
Cares for the patient and family by providing education, emotional support and tips for managing side effects
The team also need the services of a Nutritionist, physical therapist,Psychologist, clinical social worker, dentist and other health care providers.
Types of Radiation Therapy
- Radiation therapy can be delivered two ways – externally and internally.
- External beam radiation therapy delivers radiation using a linear accelerator.
- Internal radiation therapy, called brachytherapy or seed implants, involves placing radioactive sources inside the patient.
- The type of treatment used will depend on the location, size and type of cancer.
How does the doctor plan the radiation treatment?
Before starting radiation therapy, radiation oncologist will examine the patient, review the medical history and test results, and pinpoint the exact area to be treated. in a process called simulation.
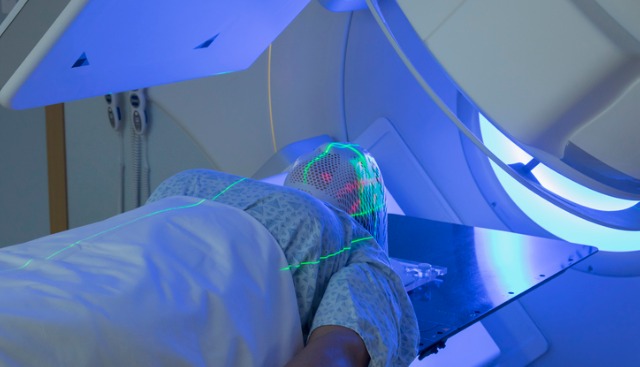
A special mold, mask, or cast of a body part might be made to make sure that the patient iss in the same position for each treatment and to help you stay still during treatment
The process is called immobilization, following which the patient is taken to MRI/CT/PET scan depending on the type of treatment planned.A planning scan is done and the images are imported to treatment planning system(TPS).The process is called simulation.Then, treatment planning is done localizing the area to be treated and dose to be delivered.
External Beam Radiation Treatment
During external beam radiation therapy, multiple beams of radiation are directed to the cancer site to destroy the cancer cells using a specialized machine called Linear accelerator.The linear accelerator is able to produce high-energy X-rays or electrons for the treatment .The Radiation beams are delivered from multiple angles and specified shapes..the treatments are typically given five days a week, Monday through Friday,over a period of 2 to 7 weeks.The total dose of external radiation therapy is usually divided into smaller doses called fractions. Weekend rest breaks allow time for normal cells to recover. The total dose of radiation and the number of treatments is based onThe site,size ,stage and type of the cancer,
Specialized types of external beam radiation therapy
Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3-D CRT)
Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, or 3-D CRT, uses computers and special imaging techniques such as CT, MRI or PET scans to show the size, shape and location of the tumor as well as surrounding organs. radiation oncologist can then precisely tailor the radiation beams to the size and shape of tumor with special shielding. Because the radiation beams are carefully targeted, nearby normal tissue receives less radiation and is able to heal better.
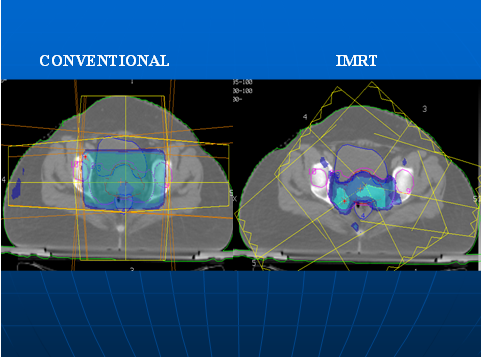
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
Intensity modulated radiation therapy, or IMRT, is a specialized form of 3-D CRT that allows radiation to be specifically shaped to cover the tumor and spare more normal tissue. With IMRT, the radiation beam can be broken up into many “beamlets,” and the intensity of each beamlet can be adjusted individually. Using IMRT, it may be possible to further limit the amount of radiation received by healthy tissue near the tumor. In some situations, this may also safely allow a higher dose of radiation to be delivered to the tumour.
Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
IGRT is used to more accurately deliver radiation to the cancer. IGRT involves conformal radiation treatment guided by imaging, such as CT, ultrasound or X-rays, taken in the treatment room just before the patient is given the radiation treatment on a daily basis.IGRT allows for better targeting of cancer cells. Radiation beams are aimed very precisely.
Stereotactic Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic radiotherapy is a specialized technique that allows radiation oncologist to use extremely focused beams of radiation to destroy certain types of tumors using higher doses than with daily radiation treatments. This treatment is usually done for small tumors.
There are two types of stereotactic radiation:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) delivers one to five stereotactic radiation treatments to the brain or spine. SRS treatment involes radiation oncology team,neurosurgeon and radiologist.
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) delivers one to five stereotactic radiation treatments to tumors within the body, excluding the brain or spine.
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is used to treat both malignant and benign conditions. The malignant(Cancerous)conditions include cancers arising in brain(recurrent gliomas),Cancers spreading to brain (Brain Metastases).Begnign tumors arising from pituitary(Pituitary adenoma),Meninges(Meningioma),Inner Ear(Acoustic Neuromas & Vestibular Schwannomas),arteriovenous malformations.It can be useful to treat painful conditions like trigeminal neuralgia.It is also helpful to treat spinal tumors.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is used to treat small tumors in the lung, liver or pelvis that cannot be removed surgically or treated with conventional radiation
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is the placement of radioactive sources in or just next to a tumor. During brachytherapy, the radioactive sources may be left in place permanently or only temporarily, depending upon the cancer.
There are two main forms of brachytherapy – intracavitary treatment and interstitial treatment. With intracavitary treatment, the radioactive sources are put into a space near where the tumor is located, such as the cervix, the vagina or the windpipe. With interstitial treatment, the radioactive sources are put directly into the tissues, such as the prostate. Another use of brachytherapy is surface mold brachytherapy, which can be used externally to treat some skin cancers.
Common side effects during radiation therapy and precautions to be taken
Radiation side effects often start during the second or third week of treatment and continue till the end of treatment. Most side effects subside within a few weeks to few months of ending treatment.Most common side effects encountered are nausea,vomiting,skinchanges,loss of appetite,fatigue,Mucositis,drymouth,altered bowel habits,low blood counts.
Nausea & Vomiting: usually seen in the initial weeks of starting the treatment, It is more if concurrent chemotherapy is administered along with radiation.It usually subsides with antiemetics and other medications prescriped by the physician.
Fatigue:Fatigue is a result of decreased appetite and low intake of food.It can be prevented by adequate intake of fluids and maintaining balanced diet.patient requires guidance of physician and nutritionist to maintain adequate diet intake.
Decreased intake of food:During the courseof treatment there is decreased intake of food due to variety of reasons including loss of appetite,mucositis,painand concurrent chemotherapy.
Skin changes: During the process of radiation,the treated area might look red, irritated, sunburned, or tanned. After a few weeks, skin might become dry,itchy, or it may peel. This is called radiation dermatitis. Most of the reactions disappear slowly after treatment ends. Sometimes, the treated skin will stay darker and hard.Appropriate skin care has to be taken during the treatment.The common precautions to be taken are to wear loose,soft clothes to prevent skin damage,avoidrubbing,scrubbing,scratching of the skin,avoiding hot water on the treated area.protect the treated area from the sun.However lukewarm water and mild soap can be used after completion of treatment.the physician may priscribe adequate medication as per the requirement
Mucositis & dry mouth: when patient is receiving radiation for head and neck,mucositis (redness of ,small ulcerations of oral mucosa & tongue)and dry mouth is commonly seen.adequate oral and dental care is needed during the treatment.It is important to rinse mouth frequently.use mouth wash prescribed by the physician.It is necessary to avoid spicy,oily,hardfood.avoid taking very hot and cold,beverages.smoking,tobacco chewing and alcohol must be avoided.it is advisable to avoid sugary snacks.the physician will prescribe appropriate medication for mucositis.using soft brush for brushing is preffered.
